Business is continuously facing evolving markets and for the reasons of expanding more and more businesses. New standards are released, old ones are adapted and new interpretations made. This makes it crucial for organizations to be up-to-date on the latest developments.
By adopting IFRS, a business can present its financial statements on the same basis as its foreign competitors, making comparisons easier. Furthermore, companies with subsidiaries in countries that require or permit IFRS may be able to use one accounting language company-wide.
In this article, we will discuss the changes and amendments of IFRS Update of standards and interpretations in issue at 31 March 2019.
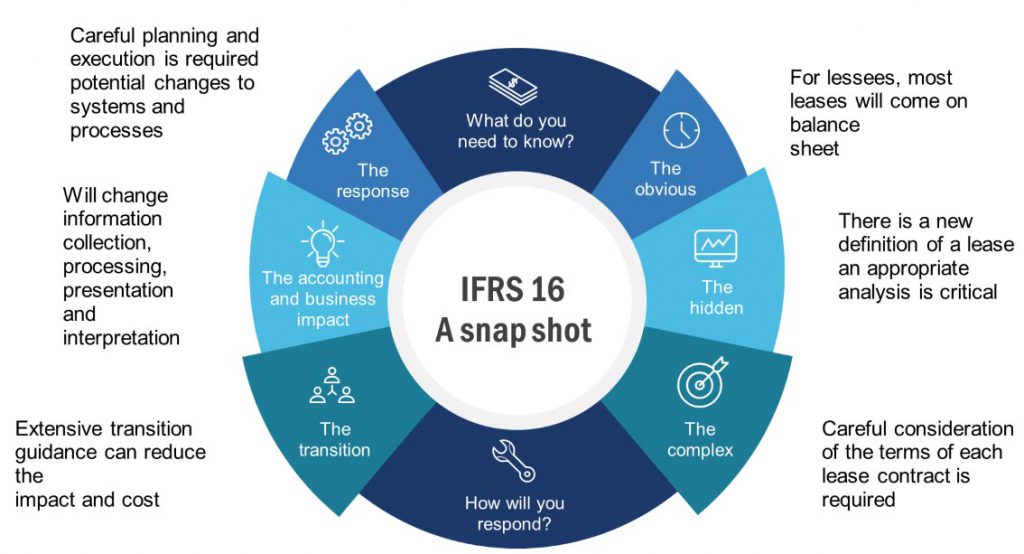
IFRS 16 Leases
Effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2019.
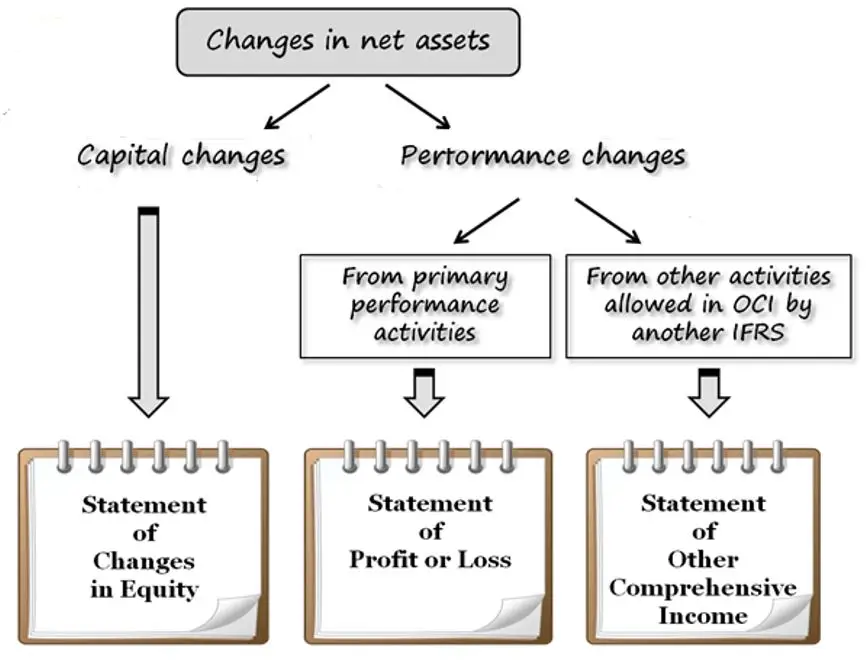
Key requirements
The scope of IFRS 16 includes leases of all assets, with certain exceptions. A lease is defined as a contract, or part of a contract, that conveys the right to use an asset (the underlying asset) for a period of time in exchange for consideration. The standard includes two recognition exemptions for lessees – leases of ’low-value’ assets (e.g., personal computers) and short-term leases (i.e., leases with a lease term of 12 months or less).
- Lessee will recognize a liability to make lease payments and an asset representing the right to use the underlying asset during the lease term.
- Lessees will be required to separately recognize the interest expense on the lease liability and the depreciation expense on the right-of-use asset.
- Lessees will be required to re-measure the lease liability upon the occurrence of certain events.
- The lessee will generally recognize the amount of the re-measurement of the lease liability as an adjustment to the right-of-use asset.
IFRS 15 Revenue from contracts with customers
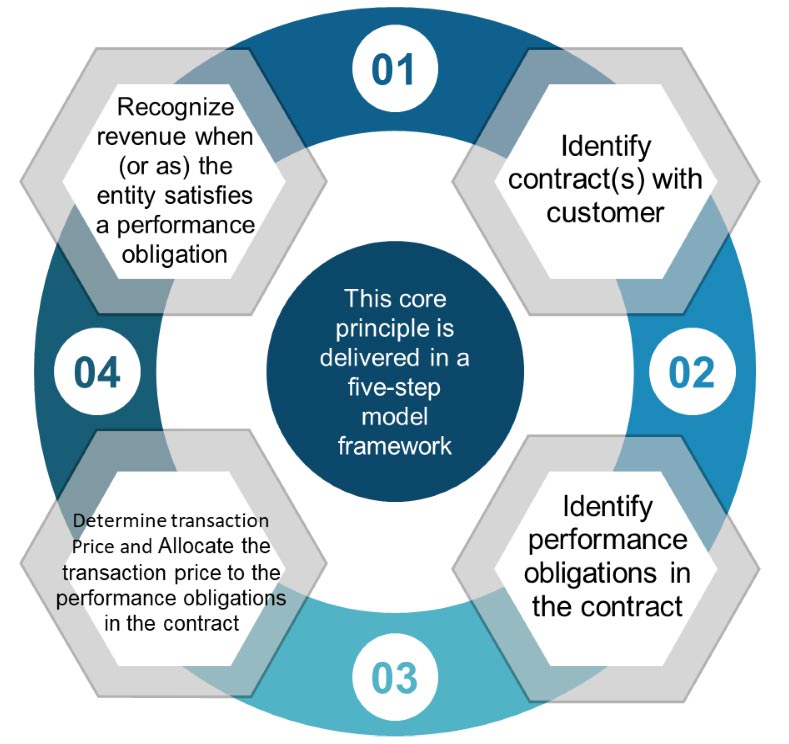
The core principle of IFRS 15 is that an entity will recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services.
IFRS 15 has replaced the previous Revenue standards IAS 18 (Revenue) and IAS 11 (Construction contracts) and their related guidance. For financial reporting, revenue recognition is arguably one of the most important and controversial topics. IFRS 15 is intended to be an improved standard for revenue recognition. IFRS 15 is mandatory for periods beginning on or after 1 January 2018.
The standard contains principles that an entity will apply to determine the measurement of revenue and timing of when it is recognized. The underlying principle is that an entity will recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers at an amount that the entity expects to be entitled to in exchange for those goods or services. The standard could significantly change how many entities recognize revenue. The standard will also result in a significant increase in the volume of disclosures related to revenue recognition.
IFRS 9 Financial Instruments:
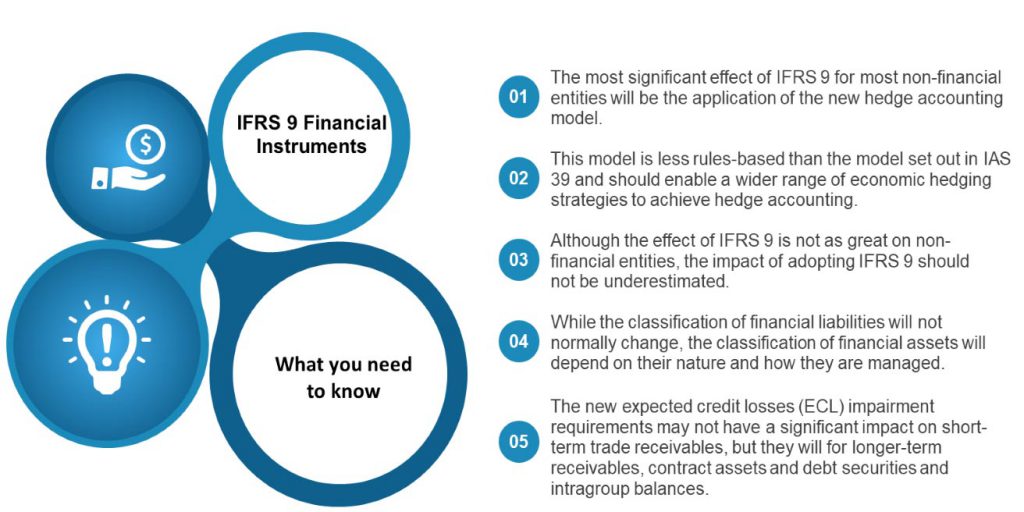
IFRS 9 Financial Instruments is the IASB’s replacement of IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement. The Standard includes requirements for recognition and measurement, impairment, derecognition and general hedge accounting.
Classification and measurement of financial instruments:
- Initial measurement of financial instruments:
All financial instruments are initially measured at fair value plus or minus
- Financial assets: subsequent measurement:
The classification of a financial asset is determined at initial recognition, however, if certain conditions are met, an asset may subsequently need to be reclassified.
- Fair value option:
IFRS 9 contains an option to designate, at initial recognition, a financial asset as measured at FVTPL if doing so eliminates or significantly reduces an ‘accounting mismatch’ that would otherwise arise from measuring assets or liabilities or recognizing the gains and losses on them on different bases. Financial assets designated at FVTPL are not subject to the reclassification requirements of IFRS 9.
- Debt instruments:
A debt instrument that meets the following two conditions must be measured at amortized cost unless the asset is designated at FVTPL under the fair value option:
- Business model test: The financial asset is held within a business model whose objective is to hold financial assets to collect their contractual cash flows.
- Cash flow characteristics test: The contractual terms of the financial asset give rise, on specified dates, to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding.
- Equity investments:
All equity investments in scope of IFRS 9 are measured at fair value in the statement of financial position, with value changes recognized in profit or loss, except for those equity investments for which the entity has elected to present value changes in other comprehensive income.
Standards Committee of the Egyptian Society of Accountants and Auditors has completed the amendment to the Egyptian accounting standards to comply with the international standards currently in force. A new Egyptian Accounting Standard for leasing contracts in accordance with Financial Leasing and Factoring Law no. 176 of 2018 signing a protocol of cooperation between FRA and the Egyptian Society of Accountants and Auditors (ESAA) The amendments issued by the Committee have introduced three Accounting Standards represented in the Egyptian Accounting Standard no. (47) For financial instruments and in accordance with IFRS 9. In addition to, the Egyptian Accounting Standard no.48 regarding revenue from contracts with customers pursuant to the International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) no. 15 to replace the Egyptian Accounting Standard no.11 related to revenue and standard no. 8 related to construction contracts. Finally, the most recent of which is the Egyptian Accounting Standard no. (49) for leasing contracts pursuant to Financial Leasing and Factoring Law no. 176 of 2018 issued in August 2018 to replace the Egyptian Accounting Standard no. (20) Related to financial leasing.